Health Benefits and Risks of Beef Steak Consumption
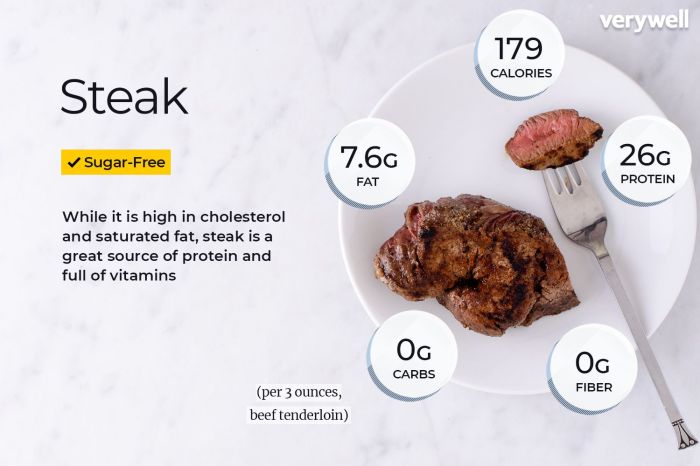
Nutrition facts of beef steak – Beef steak, a popular culinary choice, offers a rich source of nutrients but also presents potential health concerns depending on consumption patterns. Understanding both the benefits and risks associated with beef steak intake is crucial for making informed dietary choices. Moderate consumption can contribute to a healthy diet, while excessive intake may pose health challenges.
Nutritional Benefits of Moderate Beef Steak Consumption
Moderate consumption of beef steak provides significant nutritional benefits, primarily due to its high protein and iron content. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and producing enzymes and hormones. Beef is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. Furthermore, beef steak is a good source of heme iron, a form of iron readily absorbed by the body.
Heme iron is particularly important for individuals at risk of iron deficiency anemia, such as pregnant women and menstruating individuals. Adequate iron intake is crucial for oxygen transport throughout the body and preventing fatigue.
Understanding the nutrition facts of beef steak, a staple in many Maluku kitchens, requires a balanced perspective. While rich in protein and iron, it’s also high in saturated fat. For a comparison of leaner protein options, consider checking out the pulled pork nutrition facts to see how different cooking methods and cuts affect nutritional content. Returning to beef steak, mindful portion control and lean cuts are key to enjoying its flavour without compromising your health.
Health Risks Associated with Excessive Beef Steak Consumption
Excessive consumption of beef steak is linked to several potential health risks, predominantly stemming from its high saturated fat content. Saturated fat contributes to elevated levels of LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease and stroke. Studies have also indicated a possible link between high red meat consumption, including beef steak, and an increased risk of certain cancers, particularly colorectal cancer.
This association may be attributed to various factors, including the formation of heterocyclic amines (HCAs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) during cooking processes like grilling or frying at high temperatures. These compounds are known carcinogens. Additionally, excessive beef consumption can contribute to weight gain due to its high calorie and fat content.
Comparison of Benefits and Risks
| Factor | Benefits (Moderate Consumption) | Risks (Excessive Consumption) |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | Excellent source of complete protein, essential for tissue repair and growth. | High protein intake may not be beneficial for individuals with kidney disease. |
| Iron | Good source of heme iron, improving iron absorption and preventing anemia. | Not directly a risk from beef itself, but excessive iron intake can be harmful for some individuals. |
| Saturated Fat | Not a significant concern in moderation. | High saturated fat intake raises LDL cholesterol, increasing risk of cardiovascular disease. |
| Cancer Risk | No significant link demonstrated with moderate consumption. | Possible increased risk of certain cancers, particularly colorectal cancer, associated with high red meat intake. This risk is amplified by high-temperature cooking methods. |
Beef Steak in a Balanced Diet
Incorporating beef steak into a balanced diet requires mindful consideration of portion size, nutrient density, and overall dietary patterns. While beef steak offers valuable nutrients like protein and iron, it’s crucial to balance its consumption with a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats to achieve optimal nutritional intake. Overconsumption of red meat has been linked to certain health risks, emphasizing the importance of moderation and a holistic approach to nutrition.Beef steak can be successfully integrated into a healthy eating plan by considering its role within a broader context of nutrient-rich foods.
Strategic meal planning and portion control are key to maximizing the benefits while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Meal Examples Incorporating Beef Steak
The following examples demonstrate how to incorporate beef steak into balanced meals, emphasizing the combination of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats:
- Grilled Beef Steak with Quinoa and Roasted Vegetables: A lean beef steak (3-4 oz) paired with a serving of quinoa (1/2 cup cooked) provides complete protein and complex carbohydrates. Adding roasted vegetables like broccoli, bell peppers, and zucchini enhances the meal’s vitamin and mineral content.
- Beef Stir-fry with Brown Rice: Thinly sliced beef steak (3-4 oz) stir-fried with a variety of colorful vegetables (broccoli, carrots, snap peas) and a light soy-based sauce served over brown rice (1 cup cooked) offers a balanced meal rich in protein, fiber, and micronutrients.
- Beef Salad with Mixed Greens and Avocado: A smaller portion of grilled or seared beef steak (2-3 oz) can be incorporated into a salad with mixed greens, avocado, and a light vinaigrette. This meal combines protein with healthy fats and fiber from the greens and avocado.
Sample Weekly Meal Plan Incorporating Beef Steak
This sample meal plan demonstrates portion control and dietary balance, incorporating beef steak strategically across the week:
- Monday: Grilled chicken breast salad with mixed greens and a light vinaigrette; Beef steak (3 oz) with roasted sweet potatoes and asparagus.
- Tuesday: Lentil soup; Beef stir-fry with brown rice and mixed vegetables (3 oz beef).
- Wednesday: Salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli; Leftover beef stir-fry.
- Thursday: Turkey meatballs with whole-wheat pasta and marinara sauce; Side salad.
- Friday: Beef steak (4 oz) with mashed sweet potatoes and green beans; Small portion of fruit for dessert.
- Saturday: Vegetarian chili with cornbread; Small portion of beef jerky as a snack.
- Sunday: Roast chicken with roasted vegetables; Leftover vegetarian chili.
Calculating Appropriate Beef Steak Serving Size, Nutrition facts of beef steak
Determining the appropriate serving size of beef steak depends on individual factors like age, sex, activity level, and dietary goals. General guidelines suggest consuming lean cuts and limiting red meat intake to a few servings per week.
The recommended serving size of lean beef steak for most adults is typically 3-4 ounces (85-113 grams), cooked. This can be adjusted based on individual caloric needs and macronutrient targets. For example, a highly active individual may require a slightly larger portion, while someone aiming for weight loss may consume a smaller portion.
Using online calculators or consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide personalized recommendations for beef steak consumption based on specific dietary requirements and goals. These professionals can help create a balanced meal plan that integrates beef steak appropriately while meeting individual nutritional needs.
FAQ Guide: Nutrition Facts Of Beef Steak
Can I eat beef steak every day?
Daily consumption of beef steak isn’t generally recommended due to its high saturated fat content. A balanced approach, incorporating it a few times a week as part of a varied diet, is more conducive to overall well-being.
What are the best cooking methods for minimizing fat?
Lean cooking methods like grilling, broiling, or baking are preferable to frying. Trimming visible fat before cooking further reduces fat intake.
Is beef steak suitable for vegetarians or vegans?
No, beef steak is not suitable for vegetarians or vegans as it is a meat product.
How can I ensure I’m getting enough iron from beef steak?
Pairing beef steak with Vitamin C-rich foods (like citrus fruits or bell peppers) enhances iron absorption. Choose lean cuts to maximize iron intake while minimizing saturated fat.